Geiger
# Background
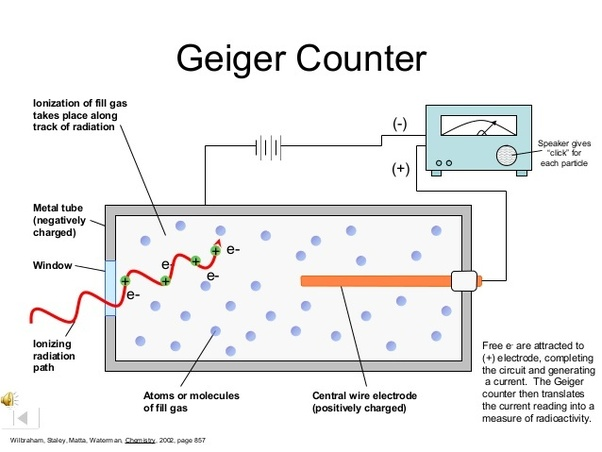
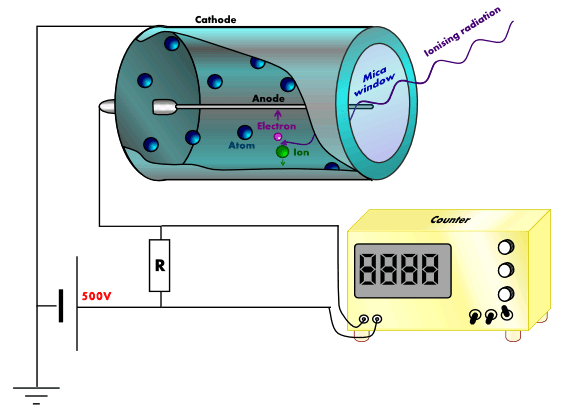
A geiger counter detects radioactive particles. Essentially, a high voltage potential is connected to a thin metal wire (anode) suspended in a vaccuum tube where the metal tube itself (cathode) is connected to ground. When a radioactive particle passes through the tube, electrons are “knocked loose” and a small temporary electric field (pulse) is generated and detected while the loose electrons move to the wire.
# Form Factors
# SBM-20

# Pancake
# Diagram